In the midst of the fourth industrial revolution, more textile brands and manufacturers are considering the shift towards advanced manufacturing technologies and automation of production by incorporating robotic sewing machines and connected systems for their softlines.But, what are the implications? How will this affect human capital?
In this blog post, we’ll dive deeper into the world of sewbots and look at a few advantages and disadvantages.
The Future of Sewbots for Softlines
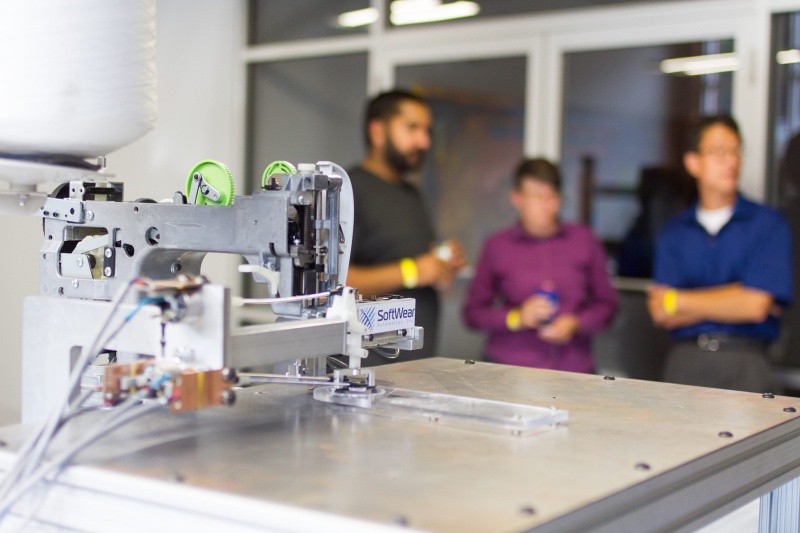
Photo: courtesy SoftWear Automation
Chinese clothing manufacturer Tianyuan Garments Company is challenging traditional apparel manufacturing with its latest employees – sewbots. The garment manufacturer has announced that its garment factory is set to be opened next year in Arkansas USA and will be operated using autonomous robots and human supervisors. The plant will be based in Little Rock and will use 21 fully automated production lines using sewbots and is expected to produce 1.2 million T-shirts annually. The production cost is incredibly competitive with garment companies that locate their manufacturing facilities in low-wage countries.
The Sewbot technology has been developed by Atlanta-based SoftWear Automation company who have been working on automation integration since 2012 after receiving a grant from the Defense Department’s technology innovation department. This led to the establishment of SoftWear Automation. The company started off selling sewbots that could produce bath mats and towels. Today, the latest fleet of sewbots are developed to manufacture a number of apparel items, including jeans and T-shirts.
The Sewbot technology uses small cameras to map soft fabrics while robots are programmed to pass material through sewing machines. According to Tianyuan Garments, the fully operational production process; from cutting and sewing fabric to the completed product, will produce one T-shirt every 22 seconds. The plan is to manufacture 800,000 T-shirts a day which is set to reduce operational costs by 33 cents per T-shirts which is a significant global competitor to cheap labor, even for the most exploitative of developing-world labor.
In a statement from SoftWear’s CEO Palaniswamy Rajan; “Factories today chase cheap labor around the world, and we have ended up with an unsustainable supply chain. SoftWear Automation’s Sewbots can move that manufacturing closer to the customer or the raw materials.” By bringing supply chains closer to consumers and reducing raw material waste, manufacturers can effectively reduce their carbon footprints and improve sustainability. According to Fashion for Good, Sewbots can lead to about a 10% reduction in carbon emissions.
Not only will automation have a positive impact on the environment, but will also have a positive effect on workers who will be able to shift towards more artisanal work.
According to Tianyuan Garment Company, the autonomous systems will not negatively impact human capital, as 3 to 5 workers will still be needed on each production line. Moreover, the workers will receive higher salaries as a result of lowered production costs.
The factory aims to employ 400 new workers next year. If automation leads to garment manufacturing being more economical in the U.S or Europe, where the environment and laborers are protected through regulation, cheap labor countries might be pressured to improve their working conditions and regulations. Some of the other benefits of sewbots include increased productivity, higher quality products, and lower costs.
Garment Industry Disruption
On the other hand, we need to discuss some of the disruptions sewbots may cause to the garment industry, particularly in countries like Bangladesh, Pakistan, and India.
According to the Clean Clothes Campaign, the 27 million jobs in these three countries could be at risk, specifically in Bangladesh as the garment industry currently employs 2.5 percent of the country’s population. The laborers are at risk of being left without jobs while mass-unemployment could lead to large-scale political destabilization. Moreover, 82% of Bangladesh’s exports consist of the apparel industry and the implementation of automation could have many unfavorable effects on the country’s economy.
While many large manufacturers may not consider the use of sewbots due to high investment, automation will also leave smaller manufacturers on the side of the road, unable to compete with powerhouses.
How do you think Sewbots will affect the global garment industry?
Do you have any questions regarding manufacturing softlines or the apparel industry in general?
Please feel free to get in touch by leaving a comment below; we’d love to hear from you!
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
{{cta(‘8a802816-7d35-40de-8006-bf8b85537c60′,’justifycenter’)}}